Digoxin Mechanism Of Action And Safe Use New Health Advisor
Search for drugs. whatever you need, whatever you want, whatever you desire, we provide. Bufotenin is a chemical constituent in the poison and eggs of several species of toads belonging to the genus bufo, but most notably in the colorado river toad (formerly bufo alvarius, now incilius alvarius) which is the only toad species in which bufotenin is present in large enough quantities for a psychoactive effect. Consider the potential onset of signs and symptoms of digoxin moa digitalis toxicity when forteo is used in patients receiving digoxin. adverse reactions the most common adverse reactions in clinical trials included: arthralgia (10. 1% forteo vs. 8. 4% placebo), pain (21. 3% forteo vs. 20. 5% placebo), and nausea (8. 5% forteo vs. 6. 7% placebo).
Digoxin belongs to a class of medications called cardiac glycosides. it works by affecting certain minerals (sodium and potassium) inside heart cells. this reduces . It’s quite an experience hearing the sound of your voice carrying out to a over 100 first year dental students. shoutout to my amazing research mentor dr. sly for easing my nerves and helping my first lecture be a success!. Despite having a unique and useful mechanism of action for patients with lower co, the dig trial failed to show a reduction in mortality in patients with heart failure. 12 however, digoxin is known digoxin moa to reduce symptoms and hospitalizations associated to heart failure, which it is why it is recommended in stage c systolic heart failure per the aha/acc guidelines. 1,12 lastly, it is important to. Sep 01, 2017 · moa: protects myocardium from toxic effects of potassium; no effect on serum potassium level. cautions: can worsen digoxin toxicity. regular insulin dosage: regular insulin 10 units iv with 50 ml of 50 percent glucose onset: 15 to 30 minutes length of effect: two to six hours.
Lanoxin Digoxin Dosing Indications Interactions Adverse
Drugs Drugs
Bufotenin Wikipedia
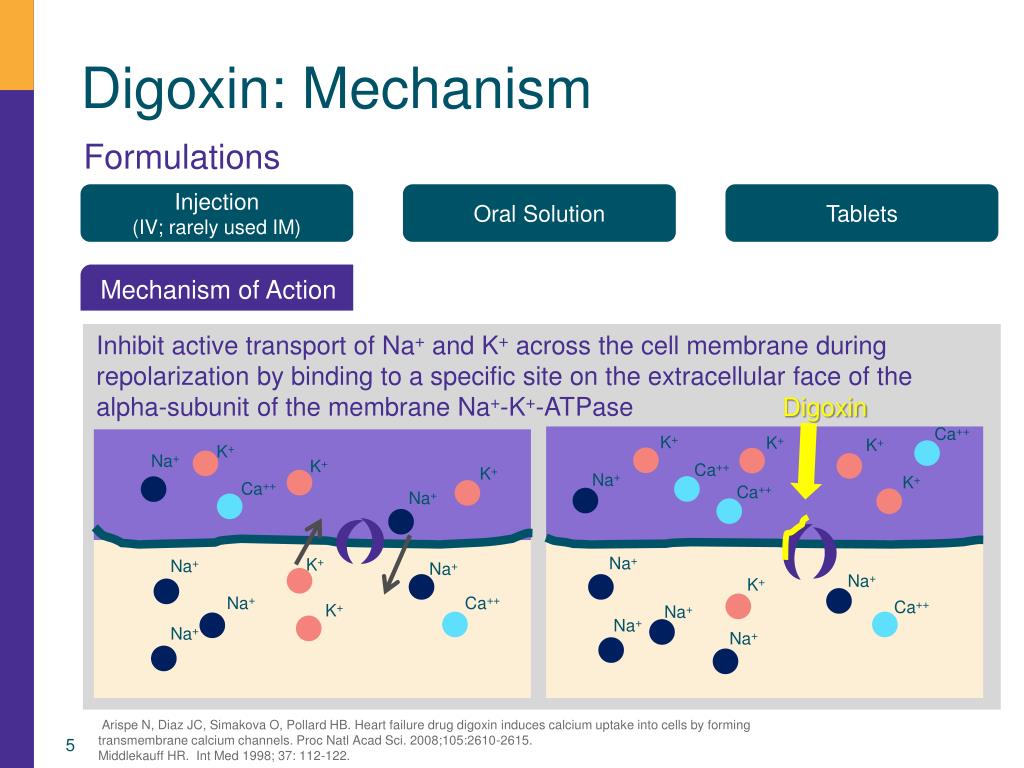
Mechanism of action. digoxin inhibits sodium-potassium atpase, an enzyme that regulates the quantity of sodium and potassium inside cells. inhibition of the enzyme leads to an increase in the intracellular concentration of sodium and thus (by stimulation of sodium-calcium exchange) an increase in the intracellular concentration of calcium. Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside that increases the force of myocardial contraction and reduces conductivity within the atrioventricular (av) node. indications and dose. rapid digitalisation, for atrial fibrillation or flutter. by mouth. for adult. 0. 75–. Digoxin stimulates the heart muscle that leads to better blood circulation. digoxin is also used for treating adults with mild to moderate congestive heart failure, atrial fibrillation, an abnormal heart rhythm, and children for increasing myocardial contractility. digoxin mechanism of action. Get your instant free coupon now. save up to 80% on prescriptions. no credit card or sign-up required to use goodrx®. it's simple to save today!.
One drug is digoxin. this medication is categorized as an antiarrhythmic drug that can help to maintain a proper heartbeat. an arrhythmia is an abnormal heartbeat. there are many different types of. Digitalis compounds, such as digoxin, are useful for reducing ventricular rate when it is being driven by a high atrial rate. the mechanism of this beneficial effect of digoxin is its ability to activate vagal efferent nerves to the heart (parasympathomimetic effect). Digoxin: mechanism of action & drug interactions instructor: adrianne baron show bio adrianne has a master's degree in cancer biology and has taught high school and college biology.
Mechanism of action digoxin inhibits sodium-potassium atpase, an enzyme that regulates the quantity of sodium and potassium inside cells. inhibition of the enzyme leads to an increase in the intracellular concentration of sodium and thus (by stimulation of sodium-calcium exchange) an increase in the intracellular concentration of calcium. More digoxin moa images. Oct 18, 2020 · digoxin beta-blockers calcium channel blockers drugs for seizures quinidine disopyramide amiodarone cimetidine paroxetine propafenone. flecainide contraindications. flecainide should not be used for patients with structural heart disease. this can include patients with coronary artery disease, a past heart attack, or with a weakened heart. See more videos for digoxin moa.
Digoxin Oral Uses Side Effects Interactions Pictures Warnings
Jan 26, 2021 digoxin · drug. a cardiac glycoside derived from the foxglove plant, digitalis purpurea · mechanism of action. direct reversible inhibition of na+/k+- . Medscape heart failure, atrial fibrillation dosing for lanoxin (digoxin), frequency -based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, mechanism of action. Mechanism of action. digoxin exerts hemodynamic, electrophysiologic, and neurohormonal effects on the cardiovascular system. 7 it reversibly inhibits the na-k atpase enzyme, leading to various beneficial effects. the na-k atpase enzyme functions to maintain the intracellular environment by regulating the entry and exit of sodium, potassium, and.
Digoxin mechanism of action. all of digoxin's actions are responsible for stabilising and preserving the electrochemical gradients of sodium and potassium ions across plasma membranes through its effects on na-k atpase. the sodium-potassium pump, or k-pump, involves energy-dependent pumping of potassium, or the active transport of the potassium. Digoxin's primary mechanism of action involves inhibition of the sodium potassium adenosine triphosphatase (na+/k+ atpase), mainly in the myocardium. this inhibition causes an increase in intracellular sodium levels, resulting in decreased activity of the sodium-calcium exchanger which normally imports three extracellular sodium ions into the cell and transports one intracellular calcium ion. By blocking a specific enzyme in the body, digoxin can help treat heart failure and atrial fibrillation. this emedtv page further explores how digoxin's mechanism of action makes the heart more efficient. a link to more detail is also included. Digoxin mechanism of action. all of digoxin's actions are responsible for stabilising and preserving the electrochemical gradients of sodium and potassium ions across plasma membranes through its effects on na-k atpase. the sodium-potassium pump, or k-pump, involves energy-dependent pumping of potassium, or the active digoxin moa transport of the potassium.
The mechanism of digoxin's (lanoxin) increase in inotropy.
Simvastatin is a lipid-lowering agent derived synthetically from a fermentation product of the fungus aspergillus terreus. hydrolyzed in vivo to an active metabolite, simvastatin competitively inhibits hepatic hydroxymethyl-glutaryl coenzyme a reductase, the enzyme which catalyzes the conversion of hmg-coa to mevalonate, a key step in cholesterol synthesis. The use of digoxin in the therapy of systolic heart failure and certain supraventricular tachycardias is controversial. mechanism of action of digitalis.
Sep 12, 2020 · 54 likes, 13 comments residents (@lapmrresidency) on instagram: “resident’s corner: name: david huy blumeyer, md year in residency: pgy-4 where were you born…”. Search for dioxin medicine. whatever you need, whatever you want, whatever you desire, we provide. Digoxin, sold under the brand name lanoxin among others, is a medication used to treat various heart conditions. most frequently it is used for atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and heart failure. digoxin is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.


0 comments:
Post a Comment